You are here
Back to topIndustry Expert Discusses Customs Procedures for Imported Fruits
On May 20, Mr. Kurt Huang, General Manager of Shanghai Oheng Import & Export Co., Ltd, gave an online lecture to listeners of Produce Report, in which he discussed Chinese Customs clearance procedures for imported fruits. The following is a summary of the key points of the lecture. For more information, please contact Khuang@fruitease.com.
1. Qualification as Consignee/Direct Importer
(i) Register with Chinese Customs as an importer/exporter.
(ii) Apply for an Import Permit on the designated item from a particular origin; this permit is restricted to a specific Importer, Origin, Item, Way of Transportation, Port of Entry, Validity Period, and Total Quantity.
2. Import Agent
Those domestic companies that are not qualified as direct importers can use a qualified import agent company and act as the consuming company during declaration to gain the double-titled tax receipt for VAT deduction on domestic sales invoicing.
3. List of Fruits with Quarantine Access and Quarantine Requirements
3.1. Requirements to Enter
(a) From the Official List
(b) From the Approved Orchard & Packing House List
The approved list of access and orchards/packing houses can be found on the AQSIQ website http://dzwjyjgs.aqsiq.gov.cn/
(c) Not Temporarily Banned
(d) Enter through Allowed Ports
3.2. Special Requirements of Quarantine Measures
(a) Cold Treatment
Cold treatment is a temperature treatment process for perishable fruits. The cold-treatment process fulfills quarantine requirements. The cold treatment parameters such as duration and fruit pulp temperature are defined in protocols established by the phytosanitary authorities in the import countries. Cold treatment is established to protect a country’s agriculture industry from unwanted insects and larvae such as the fruit fly (quoted from Hapag-Lloyd).
(b) Hot Water/Vapor Treatment
Pests of concern can be killed by dipping in hot water or hot vapor at a defined temperature for a defined period (e.g., for mangoes).
3.3. Business Impacts of Quarantine Measures
(i) Cold treatment adds export costs to every shipment. It can also easily cause chilling damage, and it makes many items almost impossible to ship. For example, South African lemons cannot withstand a pulp temperature under −0.6 °C for 24 days.
(ii) Cold treatment performed at the origin prior to shipping, followed by export by air, can result in missing the early-season market that is normally more profitable, such as for Australian mainland cherries.
(iii) Hot-water treatment can easily render mangoes too ripe to survive the limited supply chain in China.
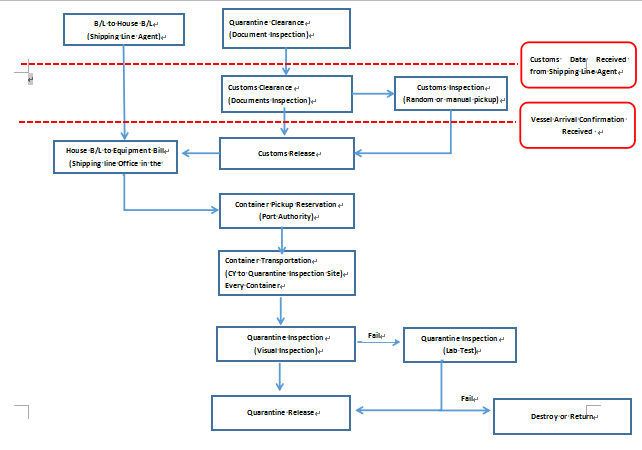
4. Clearance Procedure
[[{"fid":"416","view_mode":"default","attributes":{"height":"506","width":"696","class":"media-element file-default"},"type":"media","link_text":null}]]
5. Calculation of Import Duty and VAT
(i) Import duty charged by CIF, there is a default 0.3% insurance if quoted CNF, 13% VAT charged (CIF+duty).
(ii) Customs will impose valuation if the declared value fails the price inspection. If the Customs value is unacceptable, the importer can apply for a Price Guarantee Deposit for fast cargo release, and leave the price negotiation until later. The Guarantee Deposit will be returned or converted into tax according to the result.
(iii) If failing to provide the original Certificate of Origin, an Origin Guarantee Deposit will be collected at the equivalent of full duty, which will be returned after later presenting the original.














Add new comment